Space exploration has always captivated humanity’s imagination, pushing the boundaries of knowledge and discovery. In this pursuit, India has emerged as a prominent player, making remarkable strides in the field of space research. Today, it’s all about Chandrayaan 3!
One of India’s most notable accomplishments is the Chandrayaan mission series, which encompasses the nation’s lunar exploration efforts. This article delves into the success story of Chandrayaan-3, India’s third lunar mission, and explores its profound significance.
All About Chandrayaan 3

Chandrayaan 3 is a follow-on mission to Chandrayaan-2, which was launched in 2019. The goal of Chandrayaan 3 is to soft-land a rover on the lunar surface and conduct scientific experiments. The rover will be equipped with a variety of instruments to study the lunar surface, including a spectrometer, a camera, and a magnetometer.
The Chandrayaan 3 spacecraft consists of a propulsion module, a lander module, and a rover. The propulsion module will carry the lander and rover to the Moon. The lander module will soft-land the rover on the lunar surface. The rover will then conduct scientific experiments for up to 1 lunar day (14 Earth days).
Chandrayaan 3 Launch Date and Time
The Chandrayaan 3 mission is a significant achievement for India’s space program. It is the first time that India will attempt to soft-land a rover on the Moon. The success of this mission will pave the way for future Indian missions to the Moon, including manned missions.

Changrayaan 3 Background
India’s space program has been growing rapidly in recent years. In 2008, India became the fourth country to successfully orbit the Moon with its Chandrayaan-1 mission. Chandrayaan-2 was launched in 2019, and it successfully placed a lander and rover on the lunar surface. However, the rover was unable to deploy due to a technical problem.
The Chandrayaan 3 mission is an attempt to redeem the failure of Chandrayaan-2. The mission is also a chance for India to demonstrate its continued commitment to space exploration.
History of Chandrayaan Mission
The Chandrayaan mission program is a long-term program, and it was first conceived in the early 2000s. The first mission in the Chandrayaan program was Chandrayaan-1, which was launched in 2008. Chandrayaan-1 was a robotic mission that orbited the Moon and conducted scientific experiments. The mission was a success, and it helped to pave the way for future missions to the Moon.
The second mission in the Chandrayaan program was Chandrayaan-2, which was launched in 2019. Chandrayaan-2 was a more ambitious mission than Chandrayaan-1, and it included a rover that was intended to land on the lunar surface. However, the landing of the rover was unsuccessful, and the rover crashed on the lunar surface.
The third mission in the Chandrayaan program is Chandrayaan 3, which was launched in 2023. Chandrayaan 3 is a follow-on mission to Chandrayaan-2, and it is intended to soft-land a rover on the lunar surface. The success of Chandrayaan 3 will be a major milestone for the Chandrayaan program, and it will pave the way for future Indian missions to the Moon, including manned missions.
Chandrayaan Mission Cost
The cost of the Chandrayaan missions is a significant investment, but it is an investment that is likely to pay off in the long run. The missions have the potential to make significant contributions to our understanding of the Moon, and they could also help India to become a leading player in the field of space exploration.
- The cost of Chandrayaan 3 was Rs. 615.36 crore (approximately $75 million).
- Of that, the lander, rover and propulsion module cost Rs 250 crore and the launch services cost around Rs 365 crore.
- The cost of Chandrayaan-2 was Rs. 978 crore (approximately $141 million).
- Of that, the orbiter, lander, rover, navigation and ground support network cost Rs 603 crore and the Geo-stationary Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV Mk III) cost Rs 375 crore.
- The cost of Chandrayaan-1 was Rs. 386 crore (approximately $55 million).
The cost of the Chandrayaan missions has increased over time, due to a number of factors, including:
- The increasing complexity of the missions.
- The use of more advanced technology.
- The need to hire more skilled personnel.
- The rising cost of launch vehicles.
Despite the increasing cost, the Chandrayaan missions have been a major success for India’s space program. They have demonstrated India’s capabilities in space exploration, and they have paved the way for future Indian missions to the Moon.
ISRO Contribution
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) has made significant contributions to the Chandrayaan mission of India. ISRO designed, developed, and launched the Chandrayaan spacecraft, which consists of a propulsion module, a lander module, and a rover. ISRO also developed the instruments that the spacecraft carries, which are used to study the lunar surface, its geology, and its atmosphere. The success of the Chandrayaan mission is a testament to the hard work and dedication of the scientists and engineers at ISRO.
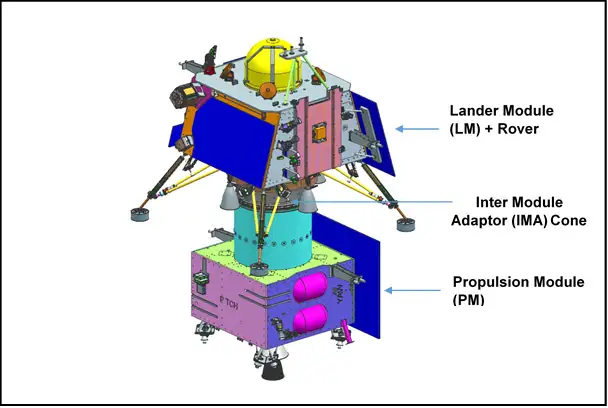
Here are some of the specific contributions that ISRO made to the Chandrayaan mission:
- Design and development of the Chandrayaan spacecraft: ISRO designed and developed the Chandrayaan spacecraft, which consists of a propulsion module, a lander module, and a rover. The spacecraft is equipped with a variety of instruments that are used to study the lunar surface, its geology, and its atmosphere.
- Development of the instruments for the Chandrayaan spacecraft: ISRO developed the instruments that the Chandrayaan spacecraft carries. These instruments include a spectrometer, a camera, a magnetometer, and a seismometer. These instruments are used to study the lunar surface, its geology, and its atmosphere.
- Launch of the Chandrayaan spacecraft: ISRO launched the Chandrayaan spacecraft on a Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark III (GSLV Mk III) rocket. The launch was successful, and the spacecraft entered orbit around the Moon.

Scientists behind Chandrayaan Mission
The Chandrayaan mission was a major undertaking that required the expertise of many scientists and engineers. Here are some of the major scientists who played a key role in the mission:
- Mylswamy Annadurai: He was the project director of Chandrayaan-1, and he played a key role in the design and development of the spacecraft. He is also a recipient of the Padma Bhushan, India’s third-highest civilian award.
- K. Radhakrishnan: He was the chairman of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) during the Chandrayaan-1 mission. He is a recipient of the Padma Vibhushan, India’s second-highest civilian award.
- Jitendra Nath Goswami: He was the principal scientific investigator of Chandrayaan-1. He is a professor at the Physical Research Laboratory in Ahmedabad, India.
- Ritu Karidhal: She was the mission director of Chandrayaan-2. She is a recipient of the Nari Shakti Puraskar, India’s highest civilian award for women.
- Muthayya Vanitha: She was the project director of Chandrayaan-2’s lander and rover. She is a recipient of the Padma Shri, India’s fourth-highest civilian award.
These are just a few of the many scientists who contributed to the Chandrayaan mission. Their hard work and dedication made the mission a success, and they helped to put India on the map as a leading spacefaring nation.
Scientific Objectives of Chandrayaan 3
The scientific objectives of Chandrayaan 3 are to:
- Soft-land a rover on the lunar surface
- Conduct scientific experiments on the lunar surface
- Study the lunar surface and its geological composition
- Search for water ice on the Moon
- Understand the evolution of the Moon
Instruments on Chandrayaan 3
The Chandrayaan 3 spacecraft is equipped with a variety of instruments to study the lunar surface, including:
- A spectrometer to study the composition of the lunar surface
- A camera to image the lunar surface
- A magnetometer to measure the magnetic field of the Moon
- A seismometer to measure moonquakes
- A laser altimeter to measure the height of the lunar surface
Significance of Chandrayaan 3
The Chandrayaan 3 mission is a significant achievement for India’s space program. It is the first time that India will attempt to soft-land a rover on the Moon. The success of this mission will pave the way for future Indian missions to the Moon, including manned missions.
The Chandrayaan 3 mission is also a source of pride for India, and it is a testament to the country’s growing capabilities in space exploration. The mission demonstrates India’s commitment to space exploration, and it is a reminder that India is a rising power in the world.
Challenges
The Chandrayaan 3 mission faces a number of challenges. The first challenge is the soft-landing of the rover on the lunar surface. The lunar surface is very uneven, and there is a risk that the rover could crash during landing.
The second challenge is the operation of the rover on the lunar surface. The lunar surface is very harsh, and there is a risk that the rover could be damaged by the environment.
The third challenge is the communication with the rover. The lunar surface is very far from Earth, and there is a delay in communication. This means that the rover will have to operate autonomously for most of the time.
Future of Chandrayaan Program
The Chandrayaan mission program is a long-term program, and there are plans for future missions to the Moon. The next mission in the Chandrayaan program is Chandrayaan 4, which is scheduled to launch in 2024. Chandrayaan 4 will be a robotic mission that will orbit the Moon and conduct scientific experiments.
There are also plans for a manned mission to the Moon as part of the Chandrayaan program. A manned mission to the Moon is a long-term goal, but it is something that India is committed to achieving.
Conclusion
The Chandrayaan program is a long-term program, and it is likely to continue for many years to come. The program has the potential to make significant contributions to our understanding of the Moon, and it could also help India to become a leading player in the field of space exploration.
The Chandrayaan Mission program is a source of pride for India, and it is a reminder that India is a rising power in the world. The program demonstrates India’s commitment to space exploration, and it is a sign of India’s growing technological prowess.
The Chandrayaan Mission program is an important part of India’s space program, and it is a testament to the country’s growing capabilities in space exploration. The program has the potential to make significant contributions to our understanding of the Moon, and it could also help India to become a leading player in the field of space exploration.
The success of the Chandrayaan program would be a major milestone for India, and it would be a source of pride for the country.








